As businesses grow and supply chains become more complex, many companies turn to logistics outsourcing to improve efficiency and reduce costs. But when it comes to choosing a logistics partner, a common question arises: 3PL vs 4PL — which model is right for your business?
Understanding the difference between these two logistics solutions is essential for making informed decisions. In this guide, we’ll break down the key distinctions between 3PL vs 4PL, how they operate, and which option may best suit your operational needs.
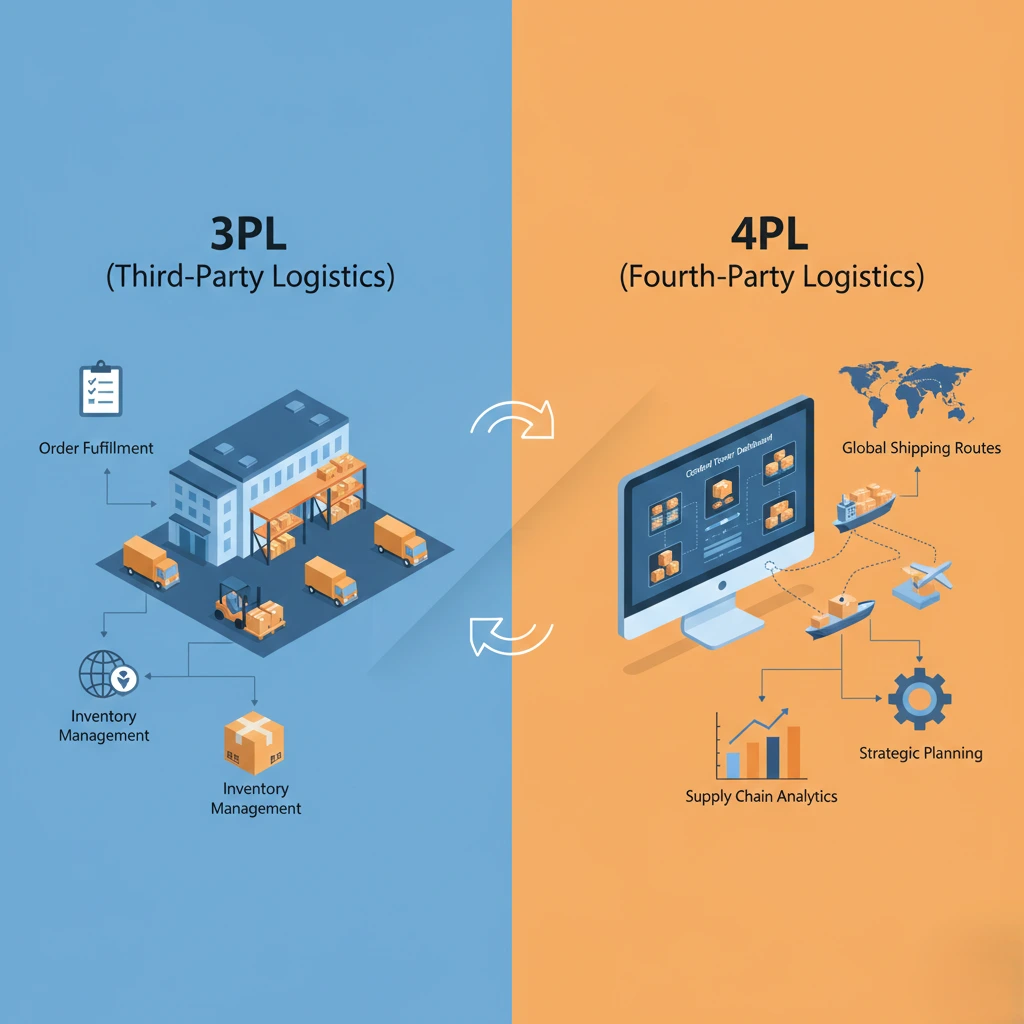
What Is 3PL?
Third party logistics (3PL) providers handle specific logistics functions on behalf of a business. These services typically include warehousing, transportation, order fulfillment, inventory management, and shipping.
Companies use third party logistics providers to manage day-to-day logistics operations without investing heavily in infrastructure. For example, an eCommerce brand may partner with a 3PL to store products in a warehouse and ship orders directly to customers.
When analyzing 3PL vs 4PL, it’s important to note that 3PL companies focus primarily on execution. They perform logistics tasks but usually do not oversee the entire supply chain strategy.
What Is 4PL?
A 4PL (Fourth Party Logistics) provider takes a more strategic and comprehensive role. Instead of simply managing transportation or warehousing, a 4PL oversees the entire supply chain. They often act as a single point of contact between the business and multiple third party logistics providers.
In the comparison of 3PL vs 4PL, a 4PL acts as a supply chain integrator. They manage logistics strategy, coordinate multiple service providers, optimize processes, and leverage technology to improve efficiency.
In many cases, a 4PL does not own warehouses or trucks. Instead, they manage resources and relationships to streamline logistics outsourcing at a higher level.
Key Differences Between 3PL and 4PL
Understanding 3PL vs 4PL requires examining several core differences.
1. Scope of Services
A 3PL typically manages specific operational tasks such as shipping, warehousing, and distribution. Their focus is on execution.
A 4PL, however, oversees the entire supply chain network. They handle coordination, strategy, analytics, and performance monitoring. In short, 3PL vs 4PL differs mainly in operational execution versus strategic management.
2. Level of Control
With a 3PL, businesses often retain significant control over logistics strategy while outsourcing operational functions.
With a 4PL, the provider assumes broader control and responsibility for logistics planning and vendor management. This makes logistics outsourcing more centralized and streamlined.
3. Complexity of Supply Chain
For smaller companies with straightforward shipping needs, a 3PL may be sufficient. However, large enterprises with global supply chains often benefit from the oversight provided in a 3PL vs 4PL comparison, where a 4PL manages multiple logistics partners under one unified strategy.
4. Technology and Data Integration
A 4PL typically offers advanced analytics, supply chain visibility tools, and integrated technology platforms. They focus on optimizing performance across all partners.
While many third party logistics providers offer technology solutions, their systems usually focus on their own operations rather than integrating multiple vendors.
Benefits of 3PL
Choosing a 3PL can offer several advantages:
- Reduced operational costs
- Access to established logistics networks
- Scalable warehousing and distribution
- Improved delivery times
For businesses new to logistics outsourcing, a 3PL often provides a practical starting point. It allows companies to focus on core competencies like marketing and product development while outsourcing fulfillment and shipping.
Benefits of 4PL
A 4PL offers benefits that go beyond execution:
- End-to-end supply chain visibility
- Strategic optimization
- Vendor management
- Improved risk management
In complex supply chains, the 3PL vs 4PL decision often comes down to whether a company needs operational support or strategic oversight. A 4PL provides holistic management that aligns logistics with long-term business goals.
Which One Should You Choose?
When evaluating 3PL vs 4PL, consider your company’s size, supply chain complexity, and internal expertise.
If you need help with warehousing, transportation, and order fulfillment, partnering with a third party logistics provider may be the right move.
If your business operates across multiple regions, works with numerous carriers, or struggles with supply chain coordination, a 4PL might provide better long-term value.
Budget also plays a role. A 4PL typically involves a higher investment but may deliver greater efficiencies in complex operations.
Final Thoughts
The debate around 3PL vs 4PL isn’t about which model is better overall—it’s about which one aligns with your business needs. A 3PL focuses on executing logistics tasks efficiently, while a 4PL provides strategic oversight and supply chain integration.
As supply chains continue to evolve, logistics outsourcing becomes increasingly important for maintaining competitiveness. By understanding the key differences between 3PL vs 4PL, businesses can choose the right partner to streamline operations, reduce costs, and support long-term growth.