In an era where consumers, regulators, and investors demand accountability, Digital Product Passports are emerging as a powerful tool to enable supply chain transparency. Businesses are no longer evaluated solely on price and quality; ethical sourcing, sustainability, and traceability now play a decisive role in brand trust. Digital Product Passports are transforming how companies share product information across the value chain, creating a more transparent, compliant, and sustainable global marketplace.
What Are Digital Product Passports
Understanding Digital Product Passports
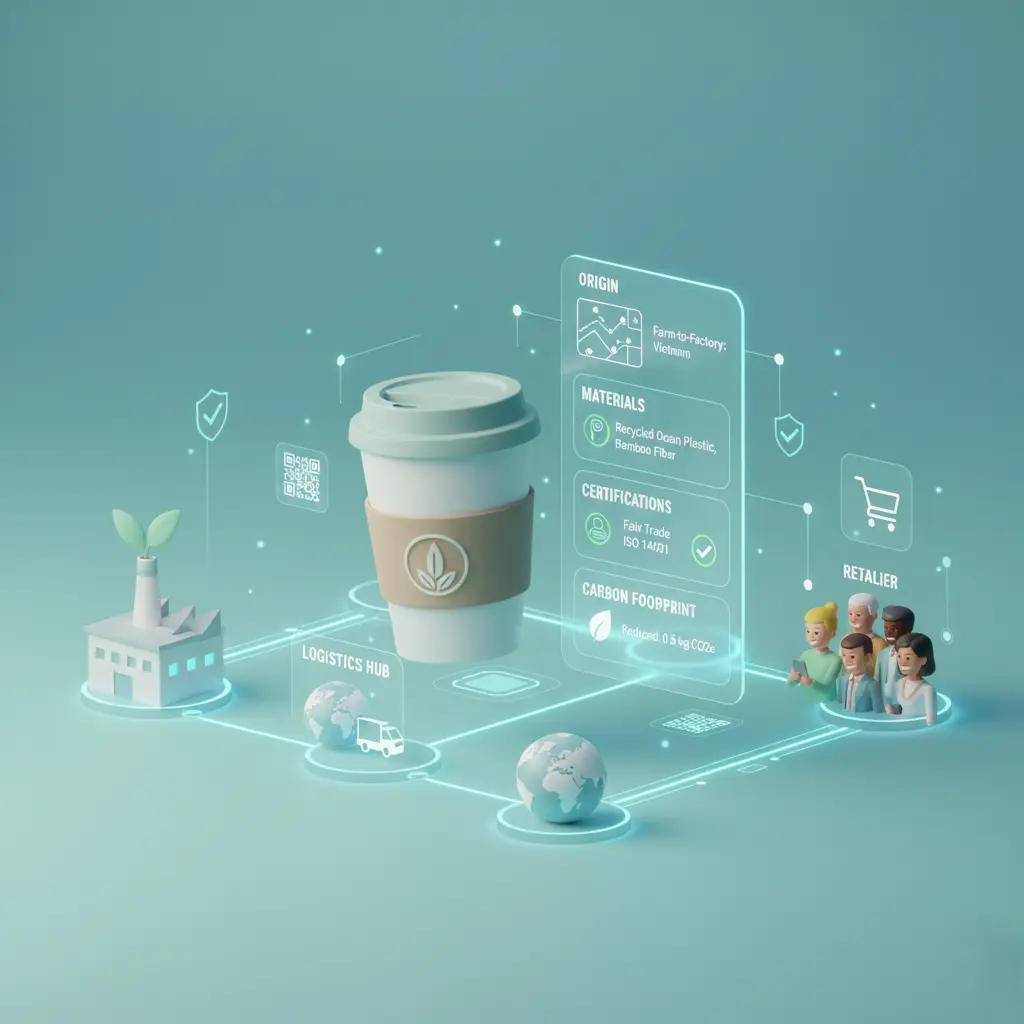
A Digital Product Passport (DPP) is a structured digital record that contains detailed information about a product throughout its lifecycle. This includes data on raw materials, manufacturing processes, certifications, environmental impact, usage instructions, and end-of-life options. By making this information accessible to stakeholders, Digital Product Passports support informed decision-making and regulatory compliance.
Why Digital Product Passports Matter Today
Governments and regulatory bodies, especially in regions like the European Union, are pushing for product traceability and transparency to support sustainability goals. Digital Product Passports help businesses comply with evolving regulations while meeting growing consumer expectations for openness and responsibility. They also improve internal efficiency by creating a single source of truth for product data.
The Role of Digital Product Passports in Supply Chain Transparency
Enhancing End-to-End Supply Chain Visibility
Supply chain transparency refers to the ability to track and share accurate information across every stage of the supply chain. Digital Product Passports provide end-to-end visibility, allowing companies to trace materials from origin to finished product. This reduces blind spots, improves risk management, and enables faster responses to disruptions or compliance issues.
Building Trust with Consumers and Partners
Transparency builds trust. When consumers can scan a QR code or access a digital record to learn where a product comes from and how it was made, confidence increases. Digital Product Passports empower brands to demonstrate authenticity, ethical sourcing, and sustainability claims with verifiable data, strengthening relationships with customers, suppliers, and regulators.
Sustainability and Circular Economy Benefits
Supporting Sustainable Product Design
Digital Product Passports play a critical role in advancing sustainability. By documenting materials, energy usage, and emissions, they help companies identify areas for improvement in product design and manufacturing. This data-driven approach enables smarter decisions that reduce environmental impact and support long-term sustainability goals.
Enabling Circular Economy Practices
A key advantage of Digital Product Passports is their support for the circular economy. Detailed product information makes it easier to repair, reuse, refurbish, and recycle products at the end of their lifecycle. This reduces waste, extends product lifespan, and helps businesses transition from linear to circular business models.
Compliance and Regulatory Advantages
Meeting Evolving Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory pressure for transparency is increasing across industries such as fashion, electronics, automotive, and manufacturing. Digital Product Passports simplify regulatory compliance by providing standardized, auditable product data. This reduces reporting complexity and minimizes the risk of penalties or reputational damage.
Improving Risk Management and Accountability
With greater visibility into suppliers and processes, companies can better identify risks related to labor practices, environmental impact, or material sourcing. Digital Product Passports enhance accountability across the supply chain, ensuring that standards are met consistently and issues are addressed proactively.
Technology Powering Digital Product Passports
Key Technologies Behind Digital Product Passports
Several technologies enable effective Digital Product Passports, including blockchain, cloud platforms, IoT sensors, and data standards. Blockchain, in particular, ensures data integrity and tamper resistance, while IoT devices provide real-time tracking of products and materials throughout the supply chain.
Integrating Digital Product Passports with Existing Systems
For maximum impact, Digital Product Passports should integrate seamlessly with ERP, supply chain management, and sustainability reporting systems. Interoperability ensures that data flows smoothly across platforms, reducing duplication and improving data accuracy across the organization.
Challenges in Implementing Digital Product Passports
Data Accuracy and Standardization
One of the main challenges in adopting Digital Product Passports is ensuring accurate and standardized data across diverse suppliers. Inconsistent data formats and varying levels of digital maturity can slow implementation. Establishing common standards and clear data governance frameworks is essential for success.
Cost and Change Management Considerations
Implementing Digital Product Passports requires investment in technology, training, and process redesign. Organizations must manage change carefully, aligning stakeholders and demonstrating the long-term value of improved supply chain transparency to secure buy-in across the business.
The Future of Digital Product Passports and Supply Chain Transparency
Driving Competitive Advantage Through Transparency
As transparency becomes a baseline expectation, companies that adopt Digital Product Passports early will gain a competitive edge. Clear, accessible product information enhances brand reputation, supports sustainability claims, and differentiates businesses in crowded markets.
Final Thoughts on Digital Product Passports
Digital Product Passports and supply chain transparency are redefining how products are created, managed, and trusted. By embracing this approach, businesses can improve compliance, support sustainability, and build stronger relationships with consumers and partners. In a world where transparency is power, Digital Product Passports are not just a compliance tool but a strategic asset for long-term success.