In today’s fast-paced ecommerce world, delivery speed plays a critical role in shaping customer satisfaction. Shoppers increasingly expect quick and reliable shipping when making online purchases. Understanding the debate of same-day vs next-day delivery is essential for online retailers seeking to meet consumer expectations and stay competitive.
Offering the right delivery options can influence purchase decisions, brand loyalty, and repeat business. By analyzing customer delivery preferences and understanding the benefits of fast shipping options, businesses can optimize their logistics strategy and improve overall customer experience.
Why Delivery Speed Matters
Fast delivery has become a key factor for online shoppers. Research shows that customers are more likely to abandon a cart if shipping is slow or unclear. The rise of platforms like Amazon and Walmart, which offer rapid delivery services, has set high expectations across the ecommerce industry.
Consumers value transparency in delivery times. Providing clear choices, whether same-day vs next-day delivery, allows customers to select what suits their schedule and urgency. Offering multiple options also caters to varying needs—from urgent orders to planned purchases.
Understanding Customer Delivery Preferences
Every shopper has unique requirements. Some prioritize speed, while others weigh cost, reliability, or convenience. A growing segment of consumers now prefers fast shipping options even if it comes at a slightly higher price.
Surveys indicate that customer delivery preferences often depend on the type of product. For example:
- Essentials or urgent items, like groceries or gifts, often require same-day delivery.
- Larger purchases or non-urgent items can be satisfied with next-day delivery.
Understanding these preferences allows retailers to optimize warehouse placement, inventory management, and courier partnerships, ensuring faster fulfillment without sacrificing efficiency.
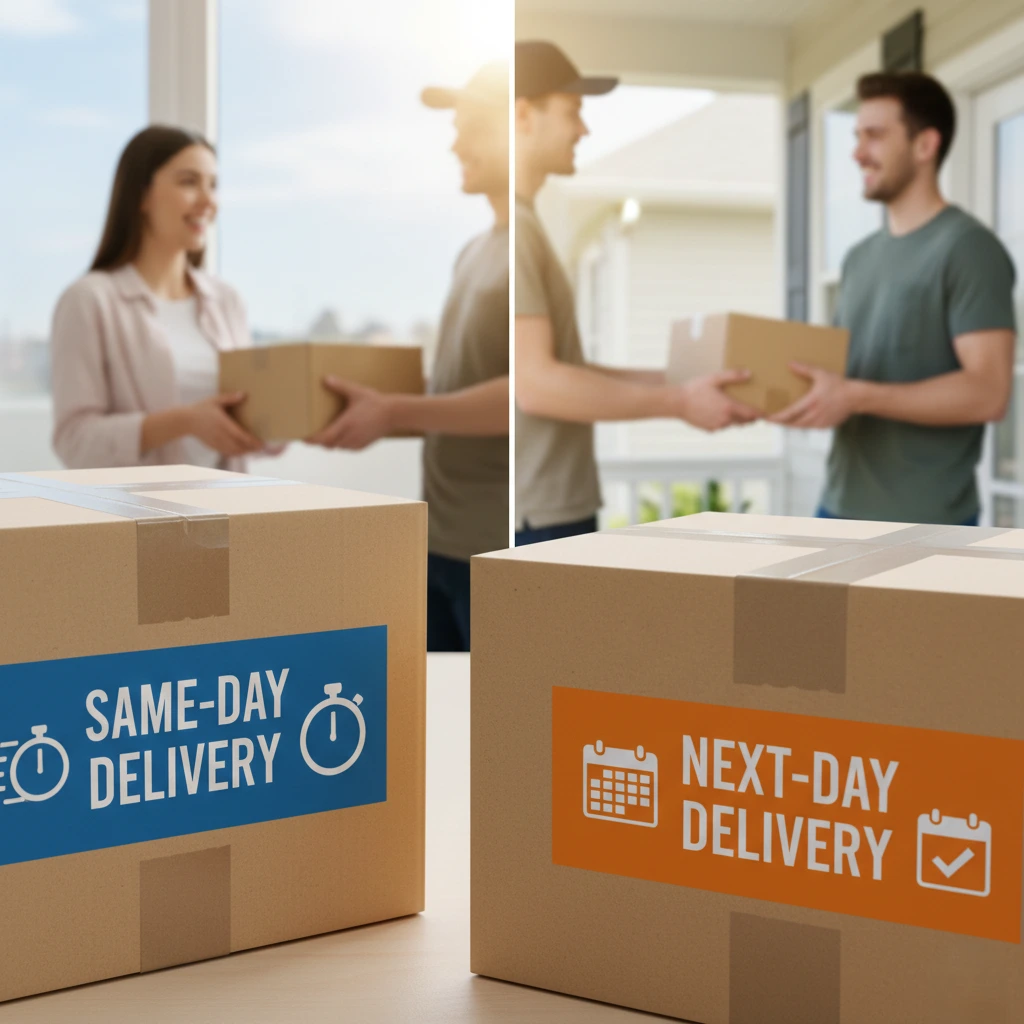
Same-Day vs Next-Day Delivery: Key Differences
Same-day delivery offers the fastest option, promising customers their order within hours. This option is ideal for urgent needs, last-minute gifts, or time-sensitive purchases.
Next-day delivery guarantees arrival by the following day, balancing speed with cost efficiency. It is suitable for customers who want fast shipping but do not require immediate fulfillment.
Retailers must consider factors such as:
- Operational capabilities: Not all businesses can manage same-day logistics efficiently.
- Cost implications: Same-day delivery often comes with higher expenses.
- Geographical coverage: Urban areas are easier to serve than rural locations.
Offering both options allows customers to choose based on urgency and budget, aligning with customer delivery preferences while maintaining operational efficiency.
Advantages of Fast Shipping Options
Investing in fast shipping options benefits both the retailer and the customer. Key advantages include:
- Increased customer satisfaction: Quick deliveries enhance the shopping experience.
- Higher conversion rates: Shoppers are more likely to complete a purchase when delivery is fast and reliable.
- Competitive advantage: Brands offering same-day vs next-day delivery stand out in a crowded market.
- Encourages repeat business: Consistently meeting or exceeding delivery expectations fosters loyalty.
By analyzing order patterns and delivery demands, businesses can implement the most effective fulfillment strategy, ensuring that speed does not compromise accuracy or quality.
Challenges of Offering Same-Day Delivery
While same-day vs next-day delivery is attractive to customers, same-day delivery presents operational challenges. Retailers must maintain:
- Sufficient inventory across multiple locations
- Efficient picking, packing, and dispatch processes
- Real-time tracking and communication systems
Despite these hurdles, the benefits of meeting urgent customer needs often outweigh the logistical complexity, especially in competitive markets.
Implementing the Right Strategy
Retailers should leverage data to understand customer delivery preferences. Key steps include:
- Segmenting customers by urgency and location
- Offering clear delivery options at checkout
- Using fulfillment centers strategically located near high-demand areas
- Communicating shipping times transparently
Balancing fast shipping options with operational costs ensures profitability while keeping customers satisfied.
Conclusion
In conclusion, same-day vs next-day delivery is more than a logistics decision—it is a critical component of the modern shopping experience. By recognizing customer delivery preferences and offering flexible fast shipping options, retailers can increase satisfaction, drive conversions, and enhance loyalty.
Businesses that successfully implement these strategies gain a competitive edge, meet rising expectations, and build trust with their customers. Whether through rapid same-day fulfillment or reliable next-day delivery, speed and convenience remain key drivers in today’s ecommerce landscape.