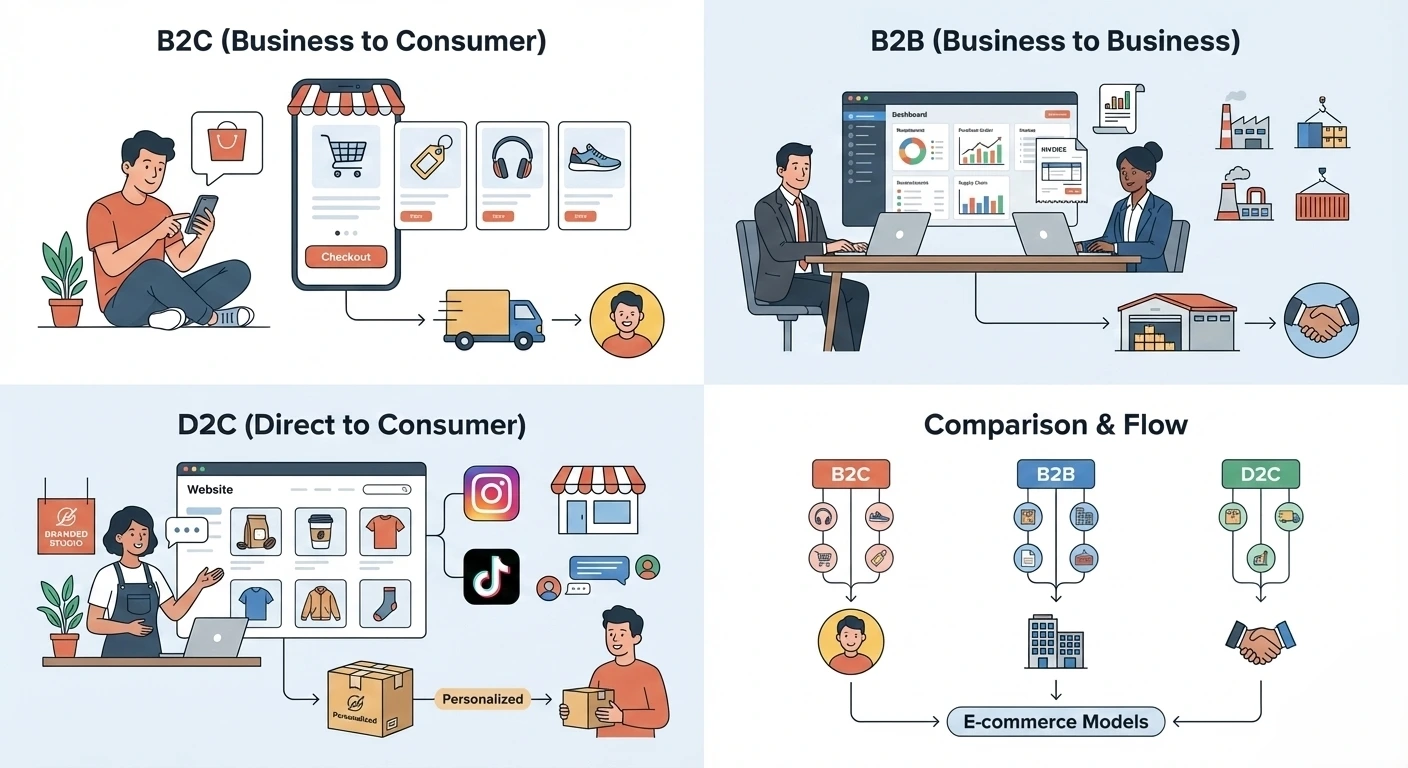
E-commerce has transformed how businesses sell products and services online. Among the most common models are B2C e-commerce, B2B e-commerce, and D2C e-commerce. While all three involve online transactions, they differ significantly in audience, strategy, marketing approach, and customer journey. Understanding these differences helps businesses choose the right model and build scalable digital strategies.
What Is B2C E-commerce
B2C e-commerce stands for Business to Consumer. In this model, companies sell products or services directly to individual consumers through online platforms.
Key Characteristics of B2C E-commerce
B2C transactions are usually quick and emotionally driven. Customers expect convenience, competitive pricing, and a seamless user experience.
Typical B2C Products
Common B2C products include fashion, electronics, beauty items, food delivery, subscriptions, and digital services.
B2C Buying Behavior
Consumers often make impulse purchases. Decisions are influenced by brand perception, reviews, promotions, and ease of checkout.
What Is B2B E-commerce
B2B e-commerce refers to Business to Business transactions, where companies sell products or services to other businesses online.
Key Characteristics of B2B E-commerce
B2B sales involve larger order values, longer sales cycles, and multiple decision makers. Pricing is often customized rather than fixed.
Typical B2B Products and Services
B2B platforms sell raw materials, office supplies, software solutions, industrial equipment, and wholesale goods.
B2B Buying Behavior
Purchasing decisions are logical and research driven. Buyers focus on value, reliability, scalability, and long term partnerships rather than impulse.
What Is D2C E-commerce
D2C e-commerce stands for Direct to Consumer. In this model, brands sell directly to consumers without intermediaries like wholesalers or marketplaces.
Key Characteristics of D2C E-commerce
D2C brands own the entire customer journey, from marketing and sales to fulfillment and support.
Typical D2C Products
D2C is popular in fashion, skincare, fitness, electronics, and niche lifestyle products.
D2C Buying Behavior
Customers are attracted by brand stories, exclusivity, personalization, and direct engagement with the brand.
Key Differences Between B2C B2B and D2C E-commerce
Understanding how these models differ helps clarify their strategic implications.
Target Audience and Relationship
B2C targets individual consumers, B2B targets organizations, and D2C targets consumers but with a deeper brand relationship. D2C brands focus heavily on community and loyalty.
Sales Cycle and Order Value
B2C and D2C usually have shorter sales cycles and lower average order values. B2B transactions involve higher values and longer decision making processes.
Pricing Strategy
B2C pricing is fixed and competitive. B2B pricing is often negotiated or volume based. D2C pricing allows higher margins by eliminating middlemen.
Marketing Approach in B2C B2B and D2C
Each model requires a distinct marketing strategy.
Marketing Strategy in B2C E-commerce
B2C marketing focuses on reach, visibility, and conversions.
Common B2C Channels
Paid ads, social media, influencer marketing, email campaigns, and marketplace optimization are widely used.
Key B2C Metrics
Click through rate, conversion rate, average order value, and customer lifetime value are critical.
Marketing Strategy in B2B E-commerce
B2B marketing emphasizes trust, education, and relationship building.
Common B2B Channels
Content marketing, SEO, LinkedIn advertising, webinars, email nurturing, and account based marketing are effective.
Key B2B Metrics
Lead quality, cost per lead, pipeline value, and conversion rates matter more than volume.
Marketing Strategy in D2C E-commerce
D2C marketing blends performance with brand building.
Common D2C Channels
Social media ads, content marketing, influencer partnerships, email, SMS, and community building drive growth.
Key D2C Metrics
Customer acquisition cost, repeat purchase rate, and brand engagement are essential.
Technology and Platform Differences
Technology needs vary across models.
B2C Technology Stack
B2C platforms focus on fast checkout, mobile optimization, and scalability.
B2B Technology Stack
B2B platforms require bulk ordering, custom pricing, CRM integration, and approval workflows.
D2C Technology Stack
D2C brands need advanced analytics, personalization tools, and customer data platforms.
Advantages and Challenges of Each Model
Every model offers unique benefits and challenges.
Advantages of B2C E-commerce
High scalability, large audiences, and faster transactions make B2C attractive.
Challenges of B2C E-commerce
High competition, rising ad costs, and low customer loyalty can limit margins.
Advantages of B2B E-commerce
Higher order values, long term contracts, and predictable revenue streams are key benefits.
Challenges of B2B E-commerce
Long sales cycles and complex decision making slow growth.
Advantages of D2C E-commerce
Higher margins, full customer ownership, and brand control drive long term value.
Challenges of D2C E-commerce
High customer acquisition costs and logistics management can be demanding.
Choosing the Right E-commerce Model
Selecting between B2C vs B2B vs D2C e-commerce depends on your product, audience, resources, and growth goals. Some businesses even combine models, such as B2B brands offering D2C storefronts.
Final Thoughts on B2C vs B2B vs D2C E-commerce
Each e-commerce model serves a distinct purpose. B2C prioritizes convenience and scale, B2B focuses on relationships and value, and D2C emphasizes brand control and customer connection. Understanding these differences helps businesses build the right strategy, choose the right platforms, and achieve sustainable growth in the evolving digital marketplace.
Leave a Reply